1.引言
图的表达方法千千万,平时选一个自己最喜欢的结构,把所有算法都在这个结构上玩通,以后遇到陌生的图结构表达,转化为自己喜欢的那个结构,然后用自己实现的算法即可。重点就是实现一个接口将陌生的图表达数据结构转化为自己熟悉的图结构表达。
2.Node类
package base_graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Node {
public int value;//节点值
public int in;//入度
public int out;//出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts;//下行的邻居节点
public ArrayList<Edge> edges;//下行边
public Node(int value) {
this.value=value;
this.in=0;
this.out=0;
this.nexts=new ArrayList<>();
this.edges=new ArrayList<>();
}
}
3.Edge类
package base_graph;
public class Edge {
public int weight;//边权
public Node from;//始边
public Node to;//终边
public Edge(int weight,Node from,Node to) {//根据提供的三元素构建一个边
this.weight=weight;
this.from=from;
this.to=to;
}
}
4.Graph类
package base_graph;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Graph {
HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;
HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes=new HashMap<>();
edges=new HashSet<>();
}
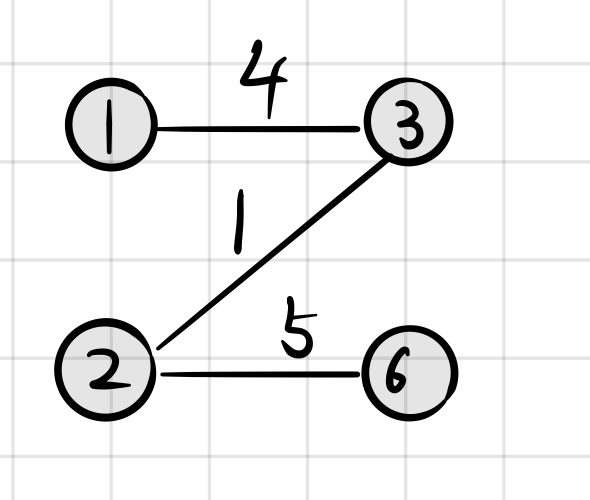
}5.将二维矩阵表示的图转化为Graph形式的图
package base_graph;
public class GenerateGraphFromMatrix {
//matrix
//weight from to
/*
* [4,1,3]
* [5,2,6]
* [1,2,3]
*/
public static Graph createGraphFromMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
Graph g=new Graph();
for(int i=0;i<matrix.length;i++) {
int weight=matrix[i][0];
int from=matrix[i][1];
int to=matrix[i][2];
if(!g.nodes.containsKey(from)) {//如果没有节点编号就去创建节点
g.nodes.put(from, new Node(from));
}
if(!g.nodes.containsKey(to)) {
g.nodes.put(to, new Node(to));
}
Node fromNode = g.nodes.get(from);//获取from节点
Node toNode=g.nodes.get(to);//获取to节点
Edge edge=new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode);//建立一条边
g.edges.add(edge);//放到g的边集合中
fromNode.nexts.add(toNode);//from节点添加下行节点
fromNode.edges.add(edge);//from 节点添加下行边
fromNode.out++;//from节点出度++
toNode.in++;//to节点入度++
}
return g;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] test = {
{4,1,3},
{5,2,6},
{1,2,3}
};
Graph graph = createGraphFromMatrix(test);
System.out.println("节点数:"+graph.nodes.size());
System.out.println("边数:"+graph.edges.size());
System.out.println("1的入度:"+graph.nodes.get(1).in+",1的出度:"+graph.nodes.get(1).out);
System.out.println("1到3的代价:"+graph.nodes.get(1).edges.get(0).weight);
System.out.println("done!");
}
}
运行结果
节点数:4
边数:3
1的入度:0,1的出度:1
1到3的代价:4
done!6.小结
本文介绍了一个非常有用的图结构的表达方法,方便在上面实现图的各种算法,并且可以很方便的将其他形式的图的表示如邻接表、邻接矩阵等转化过来,进而避免了在不同结构上重新实现图算法的繁琐操作。后续会陆续讲解基于本文定义的图结构实现的各种图算法。



